-
Overview
-
Sequence Input
-
Database Search
-
Multiple Alignment
-
Key Annotation
-
Structure Input
-
Paired
-
Tools
-
Miscellaneous
-
Statistics
-
Licence File
Quick or Basic
Quick
This is the simplest option for the user to apply. Search all fields where text can be entered in the Basic search using the operator ‘is like’.
Basic Search
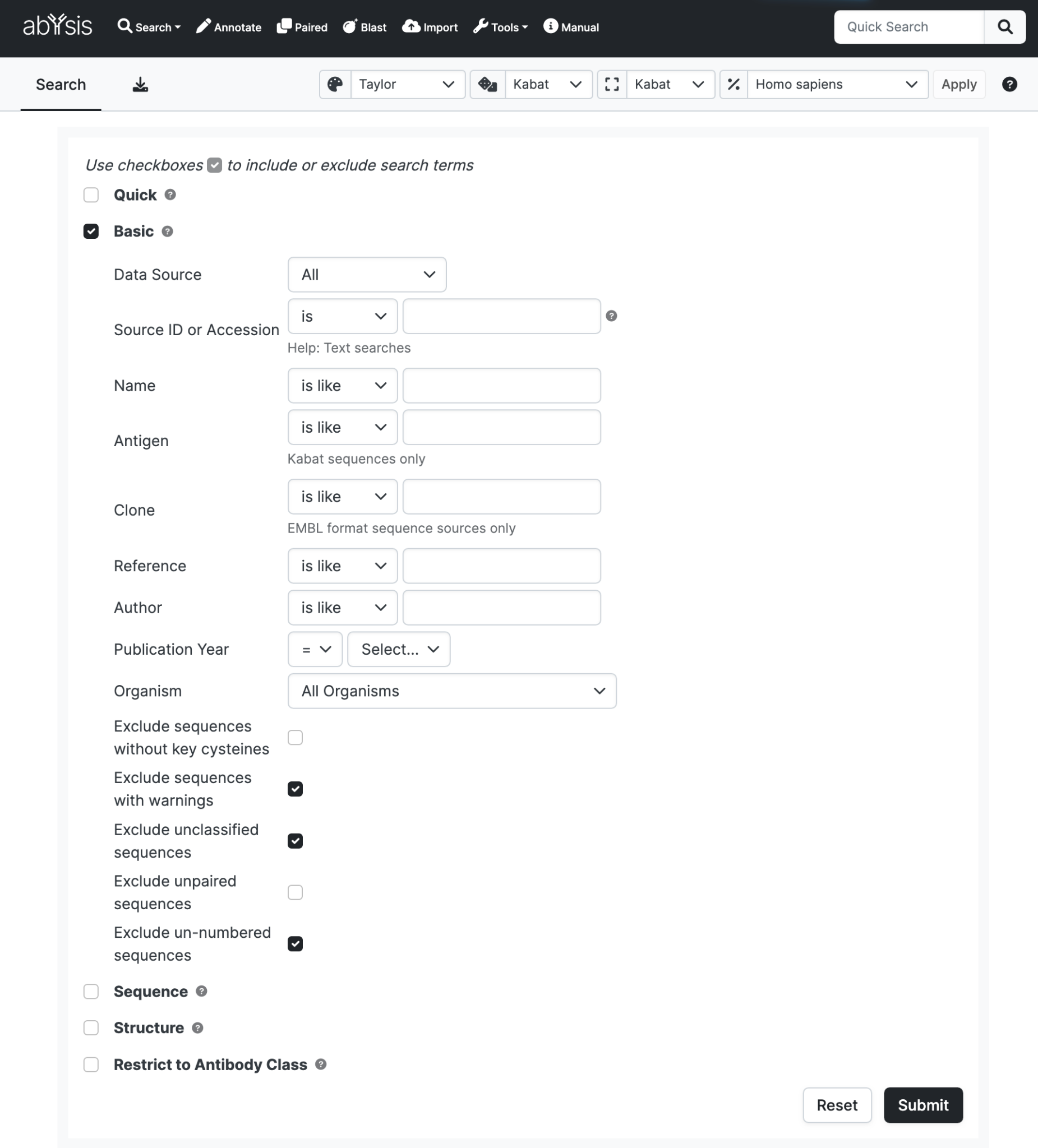
Data Source
Restrict your search to either a public data source or one of your own projects if using the Import facility.
Source ID or Accession
Source ID Primary entry-level identifier used by each Data Source. Examples include:
- For abYsis-EMBL-IG, the EMBL entry ID for each DNA entry e.g. A03900
- For PDB, the code for both protein sequence and structure e.g. 12e8
- For Kabat, an entry ID e.g. 000100
Accession Uniquely identifies a sequence in abYsis, for a given Source ID. Examples:
- For abYsis-EMBL-IG data, the protein identifier CAA00307.1
- For PDB data, the PDB ID with an underscore and chain identifier appended e.g. 12e8_L
- For Kabat, the Accession is the same as the Source ID
Note that there can be multiple protein sequences for each DNA entry in EMBL or multiple protein chains in a single PDB entry
If the Data Source does not provide a suitable sequence-level identifier and there are multiple sequences for a given Source ID, the abYsis accession uses the Source ID with an appended counter e.g. A123456 (2), A123456 (3).
Import Proprietary sequences entered by the User operate similarly.
Name
The Name field is derived from textual annotations provided by the Data Source.
Only a single search item should be entered for gene name, protein product, sequence title, mnemonic or other text description.
For example, if the Name was ‘mAb3F2 immunoglobulin gamma heavy chain’, this entry could be identified well by; ‘is like’ mAb3F2.
Antigen
Populated only for Kabat sequences as cannot be parsed automatically from other public data sources.
Only a single name or search term should be entered.
Clone
Populated only for data sources using EMBL format files.
Only a single name or search term should be entered.
Reference
Search titles and publication details of the reference and patent data associated with each sequence.
Patent data is populated only for data sources using EMBL format files.
Only a single name or search term should be entered.
Author
Search surnames of the authors of the reference data associated with each sequence.
Only a single name or search term should be entered.
Publication Year
Select a Publication Year and use the adjacent dropdown to select whether you are interested in publications before, after or during that year.
Search will be restricted to sequences with at least one publication in the specified range.
Organism
Organism names have been parsed from the data source, with some automated error checking and/or mapping via aliases.
Commercial Licencees: For Proprietary sequences you can further differentiate your entries by using your own Organism when using the Import facility. e.g. Company Mouse
The organism name stored in abYsis is almost always the species or sub-species, sometimes the genus and very occasionally a common name.
In some cases, the species will displayed two names (e.g. Homo sapiens, Mus musculus). This appears in the original data and represents a chimeric of some sort.
Searches will be restricted to organisms with that name or start with that name e.g. Rattus will allow Rattus rattus and Rattus norvegicus.
Note that species information is taken from the source data files.
Exclude sequences with warnings
A small fraction (<1%) of public data loaded into abYsis carry warnings. The bulk of these are germline DNA sequences flagged as pseudogenes or non-functional. You can avoid these by selecting Exclude.
Exclude unclassified sequences
Sequences are classified in abYsis as heavy, light, kappa or lambda using a combination of textual annotations provided by the data source and computed annotations made by abYsis. In some cases textual annotation is incomplete or ambiguous and in some cases abYsis may fail to determine a chain type. Where there is an inconsistency, the computed annotation is preferred and the sequence is tagged with a warning.
You can avoid these by selected Exclude.
Exclude unpaired sequences
Light and heavy chain sequences can be paired in abYsis. For public sequences this can be using a combination of textual annotations provided by the data source and computed annotations made by abYsis.
A cautious approach is taken to pairing to avoid incorrect pairs at the expense of missing some correct pairs.
For proprietary sequences the user must define the pairing at the time of Import.
Exclude un-numbered sequences
Sequences are un-numbered when they cannot be automatically numbering by abYsis. Not all sequences can be numbered.
For example, those with missing N-terminii beyond the first Cys and large or unusual deletions/insertions might not be numbered.
Protein sequences shorter than 70 residues are not processed through the numbering pipeline.
